Alexey Vasiliev, Railsware


 PostgreSQL ("Postgres") - is an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) with an emphasis on extensibility and standards-compliance. Based on the SQL language and supports many of the features of the standard SQL:2011. PostgreSQL evolved from the Ingres project at the University of California, Berkeley. In 1982 the leader of the Ingres team, Michael Stonebraker, left Berkeley to make a proprietary version of Ingres. He returned to Berkeley in 1985 and started a post-Ingres project
PostgreSQL ("Postgres") - is an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) with an emphasis on extensibility and standards-compliance. Based on the SQL language and supports many of the features of the standard SQL:2011. PostgreSQL evolved from the Ingres project at the University of California, Berkeley. In 1982 the leader of the Ingres team, Michael Stonebraker, left Berkeley to make a proprietary version of Ingres. He returned to Berkeley in 1985 and started a post-Ingres project

| Limit | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Database Size | Unlimited |
| Maximum Table Size | 32 TB |
| Maximum Row Size | 1.6 TB |
| Maximum Field Size | 1 GB |
| Maximum Rows per Table | Unlimited |
| Maximum Columns per Table | 250-1600 depending on column types |
| Maximum Indexes per Table | Unlimited |

Horizontal scaling means that you scale by adding more machines into your pool of resources where Vertical scaling means that you scale by adding more power (CPU, RAM) to your existing machine
Buying a bigger box is quick(ish). Redesigning software is not
37 Signals Basecamp upgraded to 128 GB DB server: don’t need to pay the complexity tax yet

CREATE TABLE my_logs(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
logdate TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
data JSON
);CREATE TABLE my_logs2015m01 (
CHECK ( logdate >= DATE '2015−01−01' AND logdate < DATE '2015−02−01' )
) INHERITS (my_logs);
CREATE INDEX my_logs2015m01_logdate ON my_logs2015m01 (logdate);$ SELECT * FROM ONLY my_logs;
id | user_id | logdate | data | some_state
----+---------+---------+------+------------
(0 rows)
$ SELECT * FROM my_logs;
id | user_id | logdate | data | some_state
----+---------+---------------------+------------------+------------
1 | 1 | 2015-10-30 00:00:00 | some data | 1
2 | 2 | 2015-02-10 00:00:00 | some data2 | 1
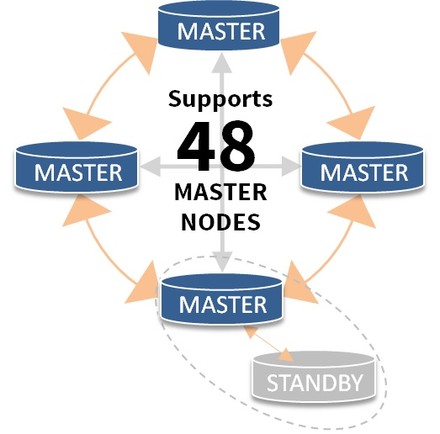
| Hot Standby | BDR | Londiste | Slony | Bucardo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Master | No | Yes | No1 | No | Yes |
| Per DB Replication | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cascading | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DDL Replication | Yes | Yes | No2 | No2 | No |
| Need external daemon | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| New table added automatically | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Use triggers | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Support updates on PK columns | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Selective replication | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Transactions applied indidualy | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |

CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION
public.get_cluster_partitions(cluster_name text)
RETURNS SETOF text AS
$BODY$
BEGIN
IF cluster_name = 'usercluster' THEN
RETURN NEXT 'dbname=plproxytest host=node1 user=postgres';
RETURN NEXT 'dbname=plproxytest host=node2 user=postgres';
RETURN;
END IF;
RAISE EXCEPTION 'Unknown cluster';
END;
$BODY$
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql' VOLATILE
COST 100
ROWS 1000;
ALTER FUNCTION public.get_cluster_partitions(text)
OWNER TO postgres;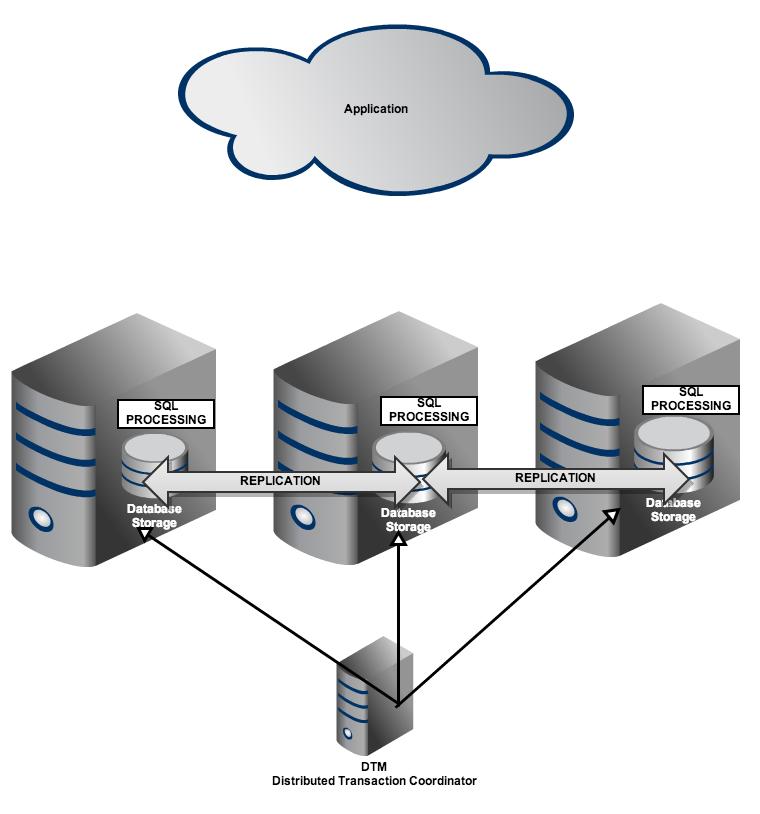
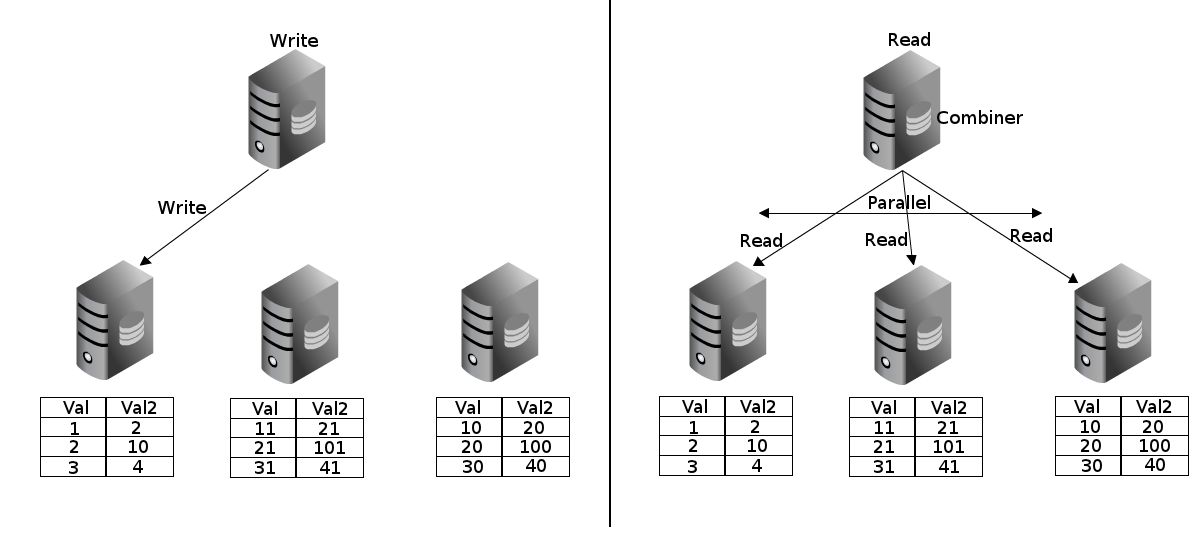
CREATE EXTENSION pg_shard;
CREATE TABLE customer_reviews
(
customer_id TEXT NOT NULL,
review_date DATE,
review_rating INTEGER
);
SELECT master_create_distributed_table('customer_reviews', 'customer_id');
SELECT master_create_worker_shards('customer_reviews', 16, 2);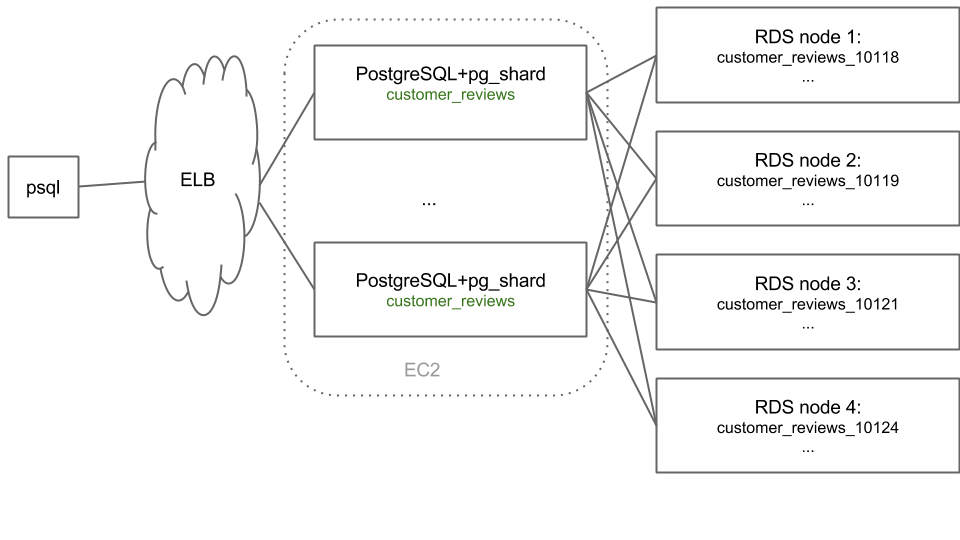


25.10.2015 - SmartMe Master class about PostgreSQL
Use promo code "RWPOD_15" for 15% discount
